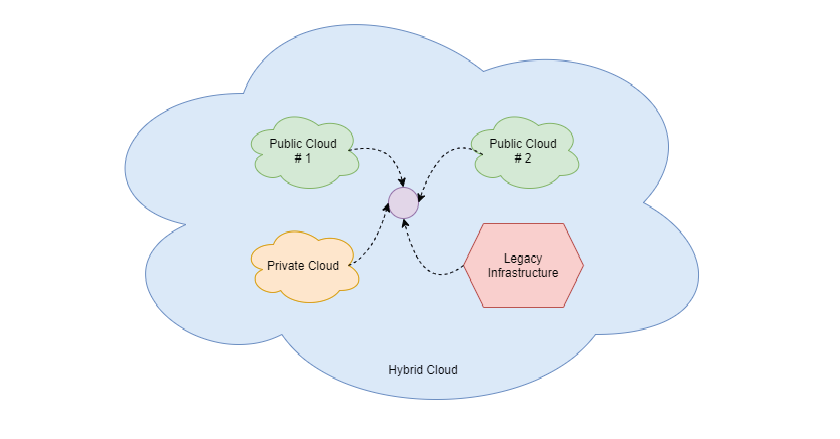
Hybrid Cloud workload combine public and private clouds. It also includes on-premises infrastructure with cloud workloads. All practical Hybrid Clouds contain different cloud environments which are tightly interconnected with each other.
Word ‘hybrid’ has its inspiration from concept of hybrid cars! Hybrid cars offer drivability through two different engines. A petrol and an electric motor. Each engine operates differently, but together both results in moving car in frugal way. Similarly, Hybrid Clouds leverage the benefits of multiple clouds for given scenario. For e.g., using SES from AWS and MS-SQL from Azure.
Hybrid Cloud combines public and private cloud resources for flexibility and security. It optimizes costs while ensuring scalability and control over sensitive data.
Why is Hybrid Cloud required?
1. Direct move from legacy to public cloud may not be practical move in many scenarios. Here migration can start with moving less risky components such as storage, emailers etc.
2. Many times, public cloud offers services which are not possible in private infrastructure. Hybrid approach is best suited for such scenarios.
3. To reduce dependency on single independent public cloud service provider. It’s very risky to put service monitoring solution on same region/zone/cloud service provider. Hybrid Cloud resolves this by having monitoring stack in some other public cloud infrastructure.
4. Making public cloud infrastructure exposed to internet & then exposing private cloud to public cloud is very well accepted security trade-off.
5. Greater control over cost by choosing best suited option from all cloud providers.